Google’s search engine is extremely important for increasing organic traffic to websites. However, certain URLs may be indexed inadvertently, resulting in irrelevant or sensitive material being shown in search results. This post will look at how to effectively delete or deindex URLs from Google that should not be indexed. You can preserve your website’s authority and improve the user experience by following these recommended practices.
Before we go into the process of removing or deindexing URLs from Google, it’s important to understand the significance of correct indexing. Crawlers are used by search engines such as Google to analyse and index online pages. Indexing is essential if you want your website to show in relevant search results, resulting in organic traffic to your online platform.
However, you may not want specific URLs to be indexed, such as private pages, duplicate material, or obsolete information. Incorrectly indexed URLs might result in a poor user experience as well as decreased search rankings. To ensure the integrity of your website’s online visibility, you must take control of what is indexed.
As SEO and high-end copywriting professionals, we understand the need to create high-quality content that not only informs but also ranks well on Google. In this detailed article, we will teach you how to remove or deindex URLs from Google that should not be indexed. Our goal is to assist you in outranking other websites and dominating search results for this key issue.
One of the most efficient ways to remove deindex URLs from Google’s index is through the Google Search Console. Follow these steps:
The first step to preventing certain URLs from being indexed is to optimize the robots.txt file. The robots.txt file guides search engine crawlers by telling them which pages they may and cannot crawl and index.
To disallow specific URLs from being indexed, add the “Disallow” directive in your robots.txt file. For example, if you want to block a page with the URL “https://www.yourwebsite.com/private-page,” your robots.txt file should include:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /private-pageThe “no index” meta tag is another efficient way to deindex particular sites. The use of no index directive in the HTML header of a certain page, you instruct search engines not to index that page.
For instance, to deindex the URL “https://www.yourwebsite.com/duplicate-content,” insert the following meta tag within the head section of the page’s HTML code:
<head>
<title>Your Page Title</title>
<meta name="robots" content="noindex">
</head>Duplicate material might harm your search engine rankings. To overcome this issue, use canonicalization, which tells search engines which version of a page is favoured when many versions exist.
Include the canonical tag pointing to the desired URL in the HTML head section of the duplicate pages:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.yourwebsite.com/preferred-version">It is critical to utilise the right HTTP status codes to signal the unavailability of URLs that no longer exist or should never be visited. A 404 status code indicates that the page could not be found, but a 410 status code indicates that the page has been permanently removed.
To avoid dead ends for visitors and search engines, always prioritise a 301 redirect for URLs that have migrated to a new location.
Low-quality or spammy backlinks might hurt your website’s rating. You can disavow such connections using Google:
Toxic Backlinks: Use tools to discover backlinks that may impair the SEO of your website.
Make a Disavow Document: Make a file with a list of URLs or domains to disavow.
domain:example.com
domain:spammywebsite.comWhen you wish to permanently relocate a page to a different site, 301 redirects are beneficial. This strategy guarantees that both people and search engines are routed to the new page:
Select a New Location: Choose the new URL to which you wish to redirect visitors.
Include the 301 Redirect: In the.htaccess file (for Apache servers), paste the following code.
Redirect 301 /old-url https://www.yourwebsite.com/new-urlSubmit the Change: Save the .htaccess file and upload it to your server.
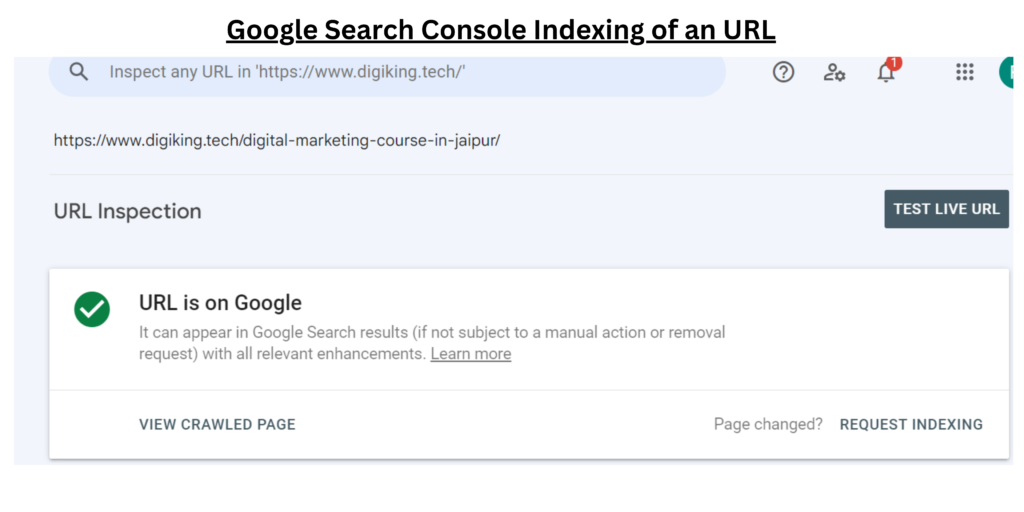
Google Search Console is a useful tool for quickly deleting URLs from Google’s index. This technique is extremely helpful when dealing with sensitive information or old stuff that must be deindexed immediately.
Log in to Google Search Console, go to the “Remove URLs” area, and submit a request to delete the URLs you wish.
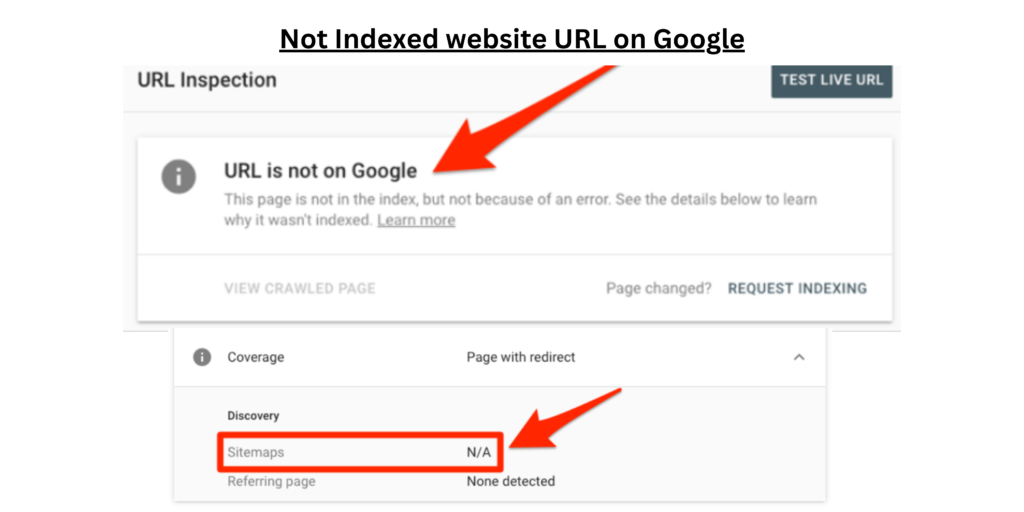
There are several reasons why you might not want your website to appear on Google. Here are a few examples:
Once a proper removal request is filed through the Google Search Console, it normally takes Google a few days to a few weeks to deindex a URL.
Deindexing a single URL will have no effect on your website’s overall rating. However, if the URL being deindexed was a critical page, it might have an impact on user experience and indirectly on rankings.
Google’s algorithms crawl and update its index on a regular basis. If your material becomes obsolete, it will be replaced with more relevant stuff. Using the “Remove Outdated Content” feature, on the other hand, helps expedite the procedure.
Simply copy and paste the URL into Google’s search field. It is indexed if the URL shows in the search results. It may not be indexed otherwise.
Removing or deindexing URLs from Google that should not be indexed is an important part of keeping your website’s SEO and authority. You can take control of your search results and give consumers with relevant and helpful material by following the procedures mentioned in this tutorial. Remember to use the Google Search Console for direct removal requests, to employ appropriate status codes and meta tags, and to remove poisonous backlinks. Review and adjust your tactics on a regular basis to guarantee a smooth and effective deindexing process.