Overview
URLs, or Uniform Resource Locators, are internet addresses that refer to specific web sites or resources. A URL’s structure is critical for both search engine optimization and user experience. By optimizing your URL structure, you can help search engines comprehend the content of your web pages and boost your website’s overall exposure.
What is URL Structure?
The organization and format of a web page’s address is referred to as URL structure. A well-structured URL offers search engines and users with useful information about the page’s content. It often includes the protocol (e.g., HTTP or HTTPS), domain name, subdirectories, filename, and any other parameters.
The URL of the webpage you’re on may be found in the address bar at the top of your browser’s window.
URL Structure Explained
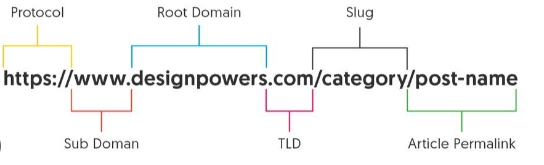
The protocol or scheme to be used to access the resource is indicated in the first portion of a URL. Protocols that are often used include “http://” for conventional web sites and “https://” for secure web pages.
A subdomain may appear before the domain name in some URLs. It is a purely optional component that often symbolises a certain area or division of the website. In the URL “blog.example.com,” for example, “blog” is the subdomain.
The domain name is the address of the website or server that hosts the resource. In the URL “www.example.com,” for example, “example.com” is the domain name.
The final portion of the domain name is the top-level domain. It denotes the sort of organisation linked with the website. TLDs include “.com,” “.org,” and “.net,” as well as country-specific TLDs like “.uk” or “.fr.”
The path denotes the precise place or directory inside a website where the required resource may be found. It follows the domain name and is denoted by slashes (“/”). In the URL “www.example.com/products/page1,” for example, “/products/page1” is the route.
Query parameters allow additional information to be passed to the server in the form of key-value pairs. They are added at the end of a URL and are followed by a question mark (“?”). Ampersands (“&”) are used to separate several parameters.
Importance of URL Structure in SEO Optimization
1. Crawlability and Indexability Improvements
online crawlers are used by search engines to locate and index online pages. A clean and optimised URL structure improves crawlers’ navigation and understanding of your website’s content easier. Search engines are more likely to rank your pages higher in search results if they can readily crawl and index them.
2. Enhancing the User Experience
A well-structured URL gives readers a preview of what they may anticipate from the web page. It should be descriptive of the material it represents. When consumers see a succinct and relevant URL, they are more inclined to click on it, enhancing the click-through rate of your website.
3. Improving Keyword Relevance
Incorporating target keywords into your URLs can assist search engines in comprehending the content and relevancy of your web pages. When consumers search for certain keywords related to your content, using those terms in your URLs can help you rank better in the search results.
4. Boosting the Click-through Rate (CTR)
When your link shows in the search results, a search-friendly URL may persuade consumers to click on it. Users are more likely to regard the website as trustworthy and relevant if it provides a clear indicator of its content, resulting in a greater click-through rate.
Effective Instructions for SEO-Optimized URLs
1. Use Descriptive and Readable URLs
Create URLs that provide a clear picture of the page’s content. Instead of using generic or unclear URLs, employ keywords that appropriately indicate the topic.
2. Target Keywords
Incorporate relevant keywords into your URLs to improve their exposure and relevancy to search engines. However, be mindful not to overdo it, as keyword stuffing might harm your SEO efforts.
3. Keep URLs Short and Simple
Long, complex URLs are difficult to remember and distribute for people, but also for search engines to interpret. Keep your URLs short and focused on the main issue.
4. Use Hyphens as Word Separators
Use hyphens (-) instead of underscores (_) or spaces to separate words in a URL. Search engines like hyphens, that facilitate the URL is more user-friendly.
5. Dynamic parameters should be avoided
Dynamic factors, such as session IDs or product filters, can lead to long and complicated URLs. Use static URLs wherever feasible since they are easier for search engines to comprehend and index.
6. Implement Correct Redirects
If you need to update the URL structure of an existing page, make sure to use suitable redirects (e.g., 301 redirects) to keep the page’s authority and prevent broken links.
Common URL Structure Mistakes to Avoid
1. Using Cryptographic Characters and IDs
Avoid using random letter or ID sequences in your URLs. They don’t supply any valuable information to consumers or search engines.
2. Stop words and extraneous words included
Remove stop words (such “and,” “the,” and “a”) and unneeded words from your URLs. Concentrate on expressing the core message of the page.
3. Failure to Keep Folder Hierarchy Proper
Maintain a reasonable folder organization in your URLs to help search engines perceive your content. It aids in the development of a clear structure for your website.
4. Ignore Canonicalization
When many URLs point to the same content, the process of selecting the preferred URL is known as canonicalization. Ignoring canonicalization can lead to duplicate content and impaired search engine rankings.
Conclusions
URL structure optimisation is critical for increasing search engine visibility and user experience on your website. By following best practises and avoiding common pitfalls, you can develop SEO-friendly URLs that will help your website rank better in search results. To maximise their usefulness, keep your URLs informative, simple, and keyword-rich.
